Mastering Attio Automations: A Complete Guide to Workflow Blocks and Billing
Unlock GTM Efficiency with Attio: Understand workflow components, AI, credit consumption, and real-world applications.
Alright, let's dive into the nitty-gritty of Attio Automations and Workflow blocks—how they function and how the billing works. As the founder of novlini®, a Growth and Product consulting agency deeply embedded in the GTM tech stack, I've seen firsthand how powerful these features can be. This is your guide to mastering Attio's automation capabilities and making sure you're optimizing your credit usage.
Attio Automations: The Engine for Your GTM Team
Attio Automations is the feature that allows you to build and automate nearly any process right inside of Attio. It's designed to give your team complete control and flexibility to automate repetitive tasks, create lead scoring systems, or implement comprehensive data integration systems. With Attio Automations, you can build systems that automatically route leads based on their potential or auto-identify customers based on their subscription and product usage data.
Key Components of Attio Workflows
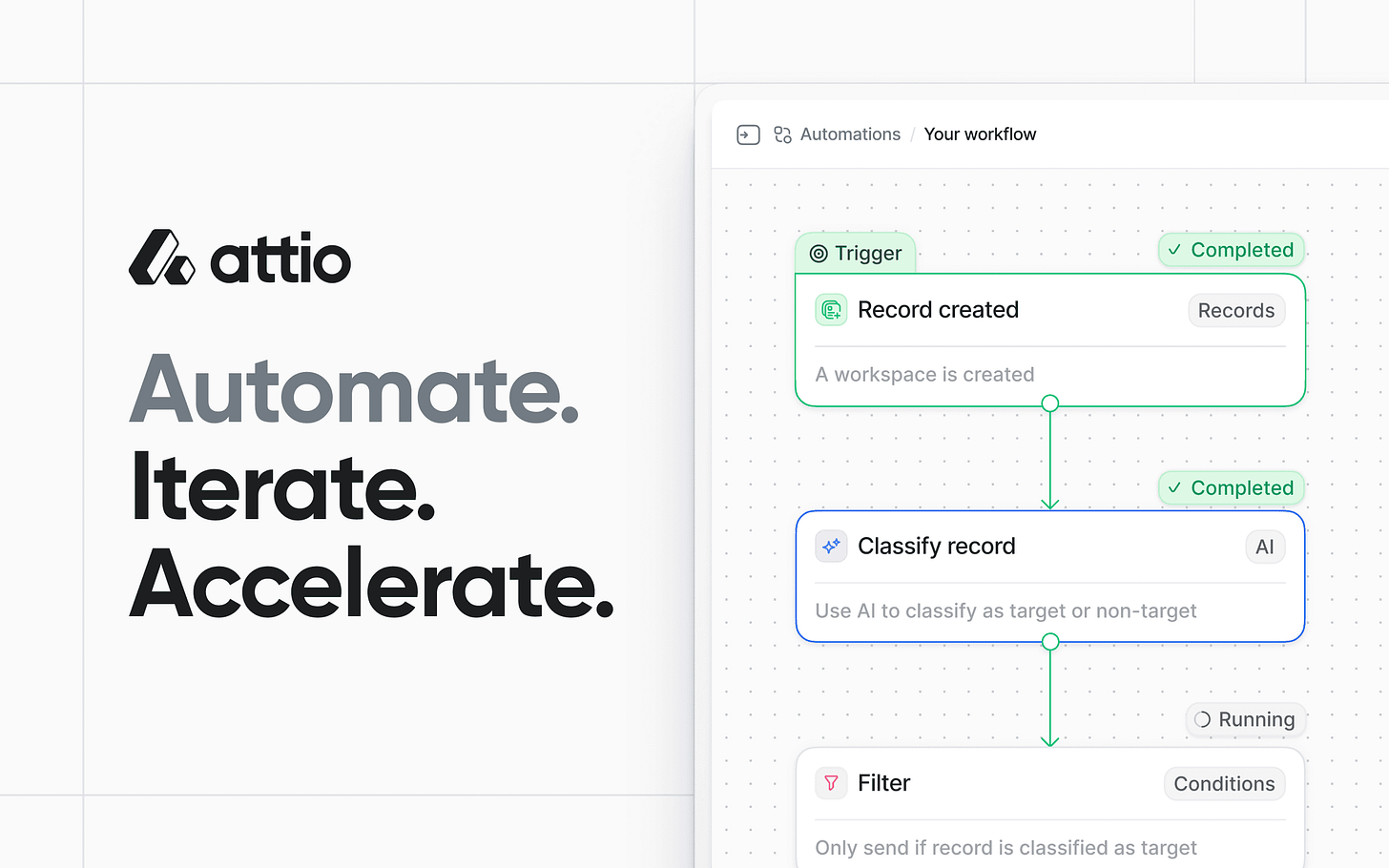
Workflows in Attio are created in a visual workflow builder. They consist of several key components:
Trigger Blocks: Every workflow starts with a trigger block, which is an event that initiates the workflow. Triggers can be based on records, lists, data, tasks, utilities, or integrations. For example, a workflow can be triggered when a deal's stage is updated. There are six types of trigger blocks in Attio: Records, Lists, Data, Tasks, Utilities, and Integrations.
Record and List Triggers:
Record/List Entry Command: Allows users to manually kick off a workflow associated with a specific record or list entry.
Record Created: Fires off a workflow any time a new record of a specific type is created.
List Entry Created: Fires off a workflow any time a record is added to a given list.
Record/List Entry Updated: Monitors changes to individual records or list entries.
Task Created Trigger: Initiates a workflow when a task is created.
Utility Triggers:
Manual Run: Used for debugging and testing workflows.
Recurring Schedule: Runs a workflow on a recurring basis, with a defined schedule.
Webhook Received: Provides a URL to which an external tool can send a webhook, triggering the workflow.
Integration Triggers:
Outreach Triggers: Trigger a workflow when a contact is added to a sequence or the state of a sequence is changed.
Typeform Trigger: Trigger a workflow when a new form response is received.
Action Blocks: After a trigger, action blocks execute specific tasks. These blocks can apply logic, perform calculations, modify records, and integrate with other applications. There are 10 different categories of action blocks: Records, Lists, Tasks, Calculations, Conditions, Delays, AI, Workspace, Utilities, and Integrations.
Conditions: Condition blocks control the execution of a workflow, determining the path a workflow should continue down or if it should stop. The three condition blocks in Attio are:
Filter: Controls whether or not a workflow continues based on a condition.
If/Else: Allows you to set your workflow down different paths based on certain conditions.
Switch: Creates multiple logic branches in a workflow.
Exploring Workflow Blocks in Detail
To truly harness the power of Attio Automations, it's essential to understand the various types of workflow blocks available. Here’s a deeper look into some key categories:
1. Records Actions
These blocks are used to create, update, and manage records within Attio.
Create Record: Creates a new record of a specified object type, populating attributes with relevant values.
Update Record: Modifies an existing record, updating specific attributes with new values.
Create or Update Record: Checks for an existing record based on a unique attribute and either updates it or creates a new one if it doesn't exist.
2. List Actions
List actions allow you to manage records within lists, which are used to organize and track records in Attio.
Add Record to List: Adds a record to a specified list, populating list-specific attributes.
Update List Entry: Modifies an existing entry in a list, updating relevant attributes.
Delete List Entry: Removes an entry from a list.
3. Task Actions
These blocks enable you to create and manage tasks, ensuring that team members are promptly reminded to complete actions.
Create Task: Generates a task with a due date, assigned user, and linked record.
4. Calculation Blocks
Calculation blocks transform existing attributes to be used in later workflow steps.
Adjust Time: Takes a timestamp and adds or subtracts a specified amount of time.
Formula: Applies mathematical transformations to numbers and currency-type attributes.
Aggregate Values: Calculates the sum, average, minimum, or maximum value of a numeric attribute from a group of records.
Random Number: Generates a random number within a specified range.
5. Condition Blocks
Condition blocks control the flow of a workflow, determining which path to follow based on specific criteria.
Filter: Checks if a record meets a certain condition, allowing the workflow to continue only if the condition is met.
If/Else: Forks the workflow into two branches based on whether a condition is true or false.
Switch: Creates multiple logic branches, allowing the workflow to follow different paths depending on which conditions are met.
6. Delay Blocks
Delay blocks add time delays to the processing of a workflow, allowing you to pause the workflow for a specified amount of time or until a specific date.
Delay: Pauses the workflow for a fixed amount of time.
Delay Until: Pauses the workflow until a specified date.
7. AI Blocks
AI blocks leverage the power of artificial intelligence to automate tasks that require human judgment.
Research Agent: Researches a record and answers questions based on data from the internet and internal sources.
Classify Text: Classifies free-form text into tags.
Summarize Record: Generates a summary of a record's attributes.
Prompt Completion: Provides an LLM (large language model) response to your custom prompt.
8. Integration Blocks
Integration blocks allow you to connect Attio with other tools in your GTM stack, such as Slack, Mixmax, Outreach, and Mailchimp.
Slack: Sends messages or actions to a Slack channel.
Outreach/Mixmax/Mailchimp: Adds people to email sequences in these platforms.
Typeform: Triggers a workflow when a new form response is received.
Examples of Attio Automations in Action
To illustrate the power of Attio Automations, let's look at a few real-world examples:
Lead Qualification: Use the Research Agent to gather data about a newly created workspace and determine if it fits your ideal customer profile (ICP). If the workspace is classified as ICP, create a new deal record and send a message on Slack to alert the sales team.
Customer Success Handover: When a deal is moved to "Closed Won," summarize the key points using the Prompt Completion block and share the summary with the customer success team on Slack.
Inbound Lead Management: When a Typeform is submitted, create or update a person record with the form data and add the person to an inbound leads list.
Automations Billing: Understanding Credits
Attio uses a credit system to measure the resource consumption of your workflows and AI attributes. Credits are consumed each time a workflow block is run or an AI attribute value is recalculated.
What is a Credit?
Credits are the currency used to measure the resource consumption of your workflows. Each workflow block consumes a credit when it runs, and credits are also consumed each time you recalculate values for an AI attribute.
How Many Credits Does My Plan Include?
The number of credits included in your plan depends on your Attio plan.
Free Plan: Includes up to 100 automations credits per month (no option to purchase additional credits).
Plus Plan: Includes up to 1000 automations credits per month, with the option to purchase more as needed.
You can view your credit usage and purchase additional credits in your workspace settings under billing.
How Do Workflow Blocks Consume Credits?
Most workflow blocks consume one credit each time they run. However, some blocks may consume more credits depending on their complexity and resource intensity.
How Do AI Attributes Consume Credits?
AI attributes consume credits each time you recalculate their values. The number of credits consumed varies depending on the type of AI attribute:
Research Agent: Uses 10 credits per run.
Summarized Record: Uses 1 credit per run.
Classify Record: Uses 1 credit per run.
Prompt Completion: Uses 1 credit per run.
Understanding how credits are consumed by different workflow blocks and AI attributes is crucial for managing your usage and optimizing your processes.
novlini's® Perspective: Maximizing Value with Attio Automations
As the founder of novlini®, I've helped numerous businesses leverage Attio Automations to streamline their GTM processes and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency. By understanding the key components of workflows, exploring the various workflow blocks, and carefully managing credit usage, you can unlock the full potential of Attio and transform your business.
If you're ready to take your Attio game to the next level, novlini® is here to help. We offer custom setup, optimization, training, and ongoing support to ensure that you're getting the most out of Attio's powerful automation capabilities. Let's work together to build the future of your GTM strategy.
Book a call with us on our website ➡️ novlini.io